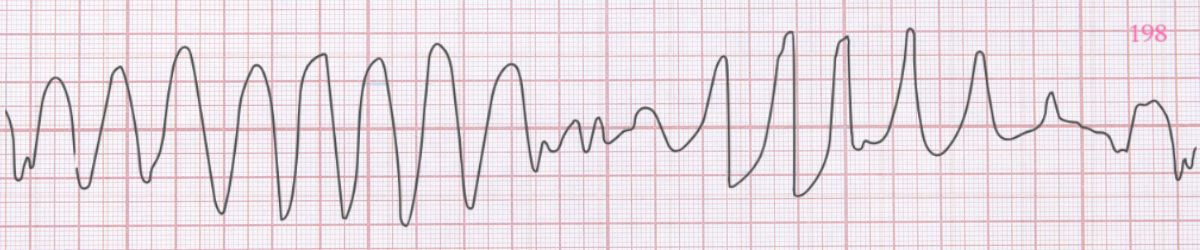
 Torsades de Pointes ECG Example
Figure 1: Torsades de Pointes - Characteristic ECG Pattern
Torsades de Pointes ECG Example
Figure 1: Torsades de Pointes - Characteristic ECG Pattern
🔑 Key Points at a Glance
- Heart Rate: 200-300 bpm
- Primary Significance: Life-threatening polymorphic VT, associated with long QT syndrome
- Key Management: Magnesium sulfate 2g IV, correct electrolytes, isoproterenol or pacing to increase heart rate
- Clinical Category: Clinical
Overview and Clinical Significance
Torsades de Pointes represents a critical cardiac rhythm pattern that requires immediate recognition and intervention. Life-threatening polymorphic VT, associated with long QT syndrome
Understanding this rhythm is essential for emergency physicians, cardiologists, intensivists, and all healthcare providers involved in acute cardiac care. Early recognition and appropriate management can significantly impact patient outcomes.
ECG Characteristics and Recognition
📊 Diagnostic ECG Criteria
- Polymorphic VT with twisting QRS axis
- Prolonged QT interval in sinus rhythm
- Characteristic twisting appearance
- Can degenerate to VFib
Systematic ECG Analysis Approach
When analyzing any ECG, including suspected Torsades de Pointes, follow this systematic approach:
- Rate: Calculate the ventricular rate using the 300-150-100-75-60-50 rule or count complexes in 6 seconds × 10
- Rhythm: Assess regularity by measuring R-R intervals across the strip
- P Waves: Identify presence, morphology, and relationship to QRS complexes
- PR Interval: Measure from start of P wave to start of QRS (normal: 0.12-0.20 seconds)
- QRS Complex: Assess duration (normal: 1mm is significant)
- T Waves: Check morphology, direction, and concordance with QRS
- QT Interval: Measure and correct for heart rate (QTc normal: Always assess hemodynamic stability before initiating treatment - unstable patients require immediate intervention regardless of the specific arrhythmia
Evidence-Based Management
Acute Management Strategy
Primary Treatment Approach: Magnesium sulfate 2g IV, correct electrolytes, isoproterenol or pacing to increase heart rate
🚨 Emergency Protocol
- Assess ABC (Airway, Breathing, Circulation) immediately
- Attach cardiac monitor and obtain 12-lead ECG
- Establish IV access and administer oxygen if SpO₂ Most recommendations for acute management of Torsades de Pointes are supported by Level A (multiple randomized trials) evidence.
Summary and Clinical Bottom Line
📋 Clinical Bottom Line
Torsades de Pointes is characterized by polymorphic vt with twisting qrs axis and prolonged qt interval in sinus rhythm. Life-threatening polymorphic VT, associated with long QT syndrome Management priority: Magnesium sulfate 2g IV, correct electrolytes, isoproterenol or pacing to increase heart rate Key takeaway: Immediate recognition and treatment are critical for patient survival
About the Author
Dr. Raj K
Emergency Medicine Physician Dr. Raj K is a board-certified Emergency Medicine physician with extensive experience in acute cardiac care and ECG interpretation. He is passionate about medical education and bringing evidence-based emergency medicine knowledge to healthcare providers worldwide through E-PulsePoints.