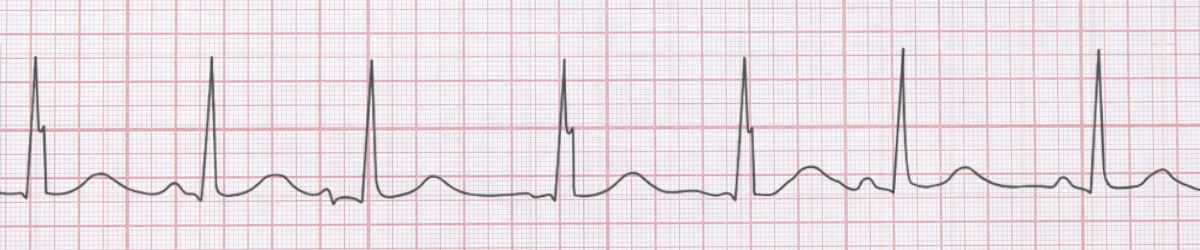
 Wandering Atrial Pacemaker ECG Example
Figure 1: Wandering Atrial Pacemaker - Characteristic ECG Pattern
Wandering Atrial Pacemaker ECG Example
Figure 1: Wandering Atrial Pacemaker - Characteristic ECG Pattern
🔑 Key Points at a Glance
- Heart Rate: 60-100 bpm
- Primary Significance: Benign variant, often seen in athletes with high vagal tone
- Key Management: No treatment required, reassurance, normal variant in athletes
- Clinical Category: Education
Overview and Clinical Significance
Wandering Atrial Pacemaker represents an important cardiac rhythm pattern that clinicians must accurately identify. Benign variant, often seen in athletes with high vagal tone
Understanding this rhythm is essential for emergency physicians, cardiologists, intensivists, and all healthcare providers involved in acute cardiac care. Early recognition and appropriate management can significantly impact patient outcomes.
ECG Characteristics and Recognition
📊 Diagnostic ECG Criteria
- ≥3 different P wave morphologies
- Variable PR intervals
- Irregular rhythm
- Normal QRS complexes
Systematic ECG Analysis Approach
When analyzing any ECG, including suspected Wandering Atrial Pacemaker, follow this systematic approach:
- Rate: Calculate the ventricular rate using the 300-150-100-75-60-50 rule or count complexes in 6 seconds × 10
- Rhythm: Assess regularity by measuring R-R intervals across the strip
- P Waves: Identify presence, morphology, and relationship to QRS complexes
- PR Interval: Measure from start of P wave to start of QRS (normal: 0.12-0.20 seconds)
- QRS Complex: Assess duration (normal: 1mm is significant)
- T Waves: Check morphology, direction, and concordance with QRS
- QT Interval: Measure and correct for heart rate (QTc normal: Correlate ECG findings with clinical presentation - the patient, not the monitor, determines management urgency
Evidence-Based Management
Acute Management Strategy
Primary Treatment Approach: No treatment required, reassurance, normal variant in athletes
Pharmacologic Interventions
Most cases require no pharmacologic intervention - focus on treating underlying causes and monitoring for progression.
Procedural Considerations
Procedural intervention is rarely required - conservative management is typically appropriate.
Differential Diagnosis
🔍 Consider These Mimics
- Consider other arrhythmias based on clinical context
Complications and Risk Stratification
Potential complications associated with Wandering Atrial Pacemaker include:
- Progression to more severe conduction abnormalities
- Symptoms interfering with quality of life
Long-Term Management and Follow-Up
Regular outpatient follow-up with cardiology or electrophysiology is recommended to monitor for progression and optimize therapy.
📅 Follow-Up Recommendations
- Cardiology follow-up within 2-4 weeks
- Consider Holter monitor or event recorder for recurrent symptoms
- Lifestyle modifications: exercise, stress reduction, avoid triggers
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
⚠️ Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failing to correlate ECG with clinical presentation
- Missing underlying reversible causes
- Not consulting cardiology when uncertain
Patient Education and Counseling
When counseling patients diagnosed with Wandering Atrial Pacemaker, address the following key points:
- Nature of the condition: Explain the rhythm abnormality in simple terms, avoiding medical jargon
- Prognosis: Provide realistic expectations about symptom control and quality of life
- Warning signs: Educate about symptoms requiring immediate medical attention (chest pain, syncope, severe dyspnea)
- Medication compliance: Importance of taking prescribed medications as directed
- Lifestyle modifications: Limit caffeine and alcohol, maintain healthy weight, exercise regularly (as tolerated), stress reduction
- Activity restrictions: Generally no restrictions once symptoms controlled
Evidence-Based Guidelines and References
Current management of Wandering Atrial Pacemaker is based on evidence from major clinical trials and consensus guidelines from professional societies including:
- American Heart Association (AHA) / American College of Cardiology (ACC) Guidelines
- European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Guidelines
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Protocols
- Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) Expert Consensus Statements
📚 Level of Evidence
Most recommendations for acute management of Wandering Atrial Pacemaker are supported by Level B (limited randomized trials or observational studies) evidence.
Summary and Clinical Bottom Line
📋 Clinical Bottom Line
Wandering Atrial Pacemaker is characterized by ≥3 different p wave morphologies and variable pr intervals. Benign variant, often seen in athletes with high vagal tone Management priority: No treatment required, reassurance, normal variant in athletes Key takeaway: Prompt diagnosis and appropriate therapy optimize outcomes
About the Author
Dr. Raj K
Emergency Medicine Physician Dr. Raj K is a board-certified Emergency Medicine physician with extensive experience in acute cardiac care and ECG interpretation. He is passionate about medical education and bringing evidence-based emergency medicine knowledge to healthcare providers worldwide through E-PulsePoints.