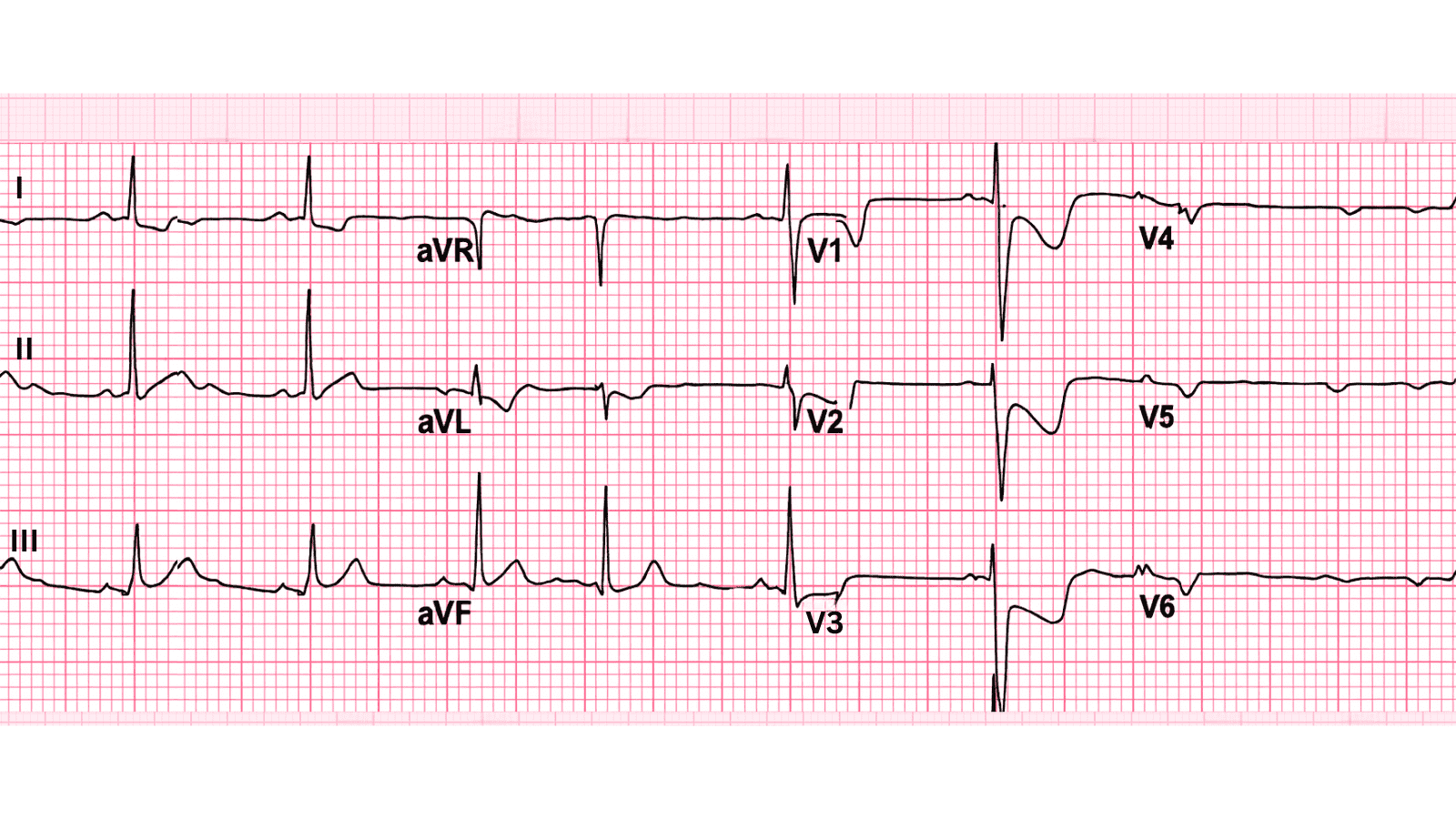
 Posterior Wall Myocardial Infarction ECG Example
Figure 1: Posterior Wall Myocardial Infarction - Characteristic ECG Pattern
Posterior Wall Myocardial Infarction ECG Example
Figure 1: Posterior Wall Myocardial Infarction - Characteristic ECG Pattern
🔑 Key Points at a Glance
- Heart Rate: Variable
- Primary Significance: Often missed, RCA or circumflex occlusion, isolated posterior MI is rare, use posterior leads V7-V9 for confirmation
- Key Management: STEMI protocol if confirmed with posterior leads showing ST elevation, emergent cardiac catheterization
- Clinical Category: Clinical
Overview and Clinical Significance
Posterior Wall Myocardial Infarction represents a critical cardiac rhythm pattern that requires immediate recognition and intervention. Often missed, RCA or circumflex occlusion, isolated posterior MI is rare, use posterior leads V7-V9 for confirmation
Understanding this ECG finding is essential for emergency physicians, cardiologists, intensivists, and all healthcare providers involved in acute cardiac care. Early recognition and appropriate management can significantly impact patient outcomes and prevent life-threatening complications.
ECG Characteristics and Recognition
📊 Diagnostic ECG Criteria
- Tall R waves in V1-V2 (mirror image)
- ST depression in V1-V3 (reciprocal)
- Upright T waves in V1-V2
- Associated inferior or lateral MI often present
Systematic ECG Analysis Approach
When analyzing any ECG, including suspected Posterior Wall Myocardial Infarction, follow this systematic approach:
- Rate: Calculate ventricular rate using the 300-150-100-75-60-50 rule or count QRS complexes in 6 seconds × 10
- Rhythm: Assess regularity by measuring R-R intervals across the entire strip
- P Waves: Identify presence, morphology, and relationship to QRS complexes
- PR Interval: Measure from start of P wave to start of QRS (normal: 0.12-0.20 seconds or 3-5 small squares)
- QRS Complex: Assess duration (normal: Always assess hemodynamic stability FIRST - unstable patients require immediate intervention regardless of the specific ECG diagnosis
Evidence-Based Management
Acute Management Strategy
Primary Treatment Approach: STEMI protocol if confirmed with posterior leads showing ST elevation, emergent cardiac catheterization
🚨 Emergency Protocol - Time-Critical Actions
- Immediate ABC assessment (Airway, Breathing, Circulation)
- Attach continuous cardiac monitoring and obtain 12-lead ECG
- Establish large-bore IV access (×2) and check bedside glucose
- Administer supplemental oxygen if SpO₂ Recommendations for management of Posterior Wall Myocardial Infarction are primarily supported by Level A evidence (multiple high-quality randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses).
Summary and Clinical Bottom Line
📋 Clinical Bottom Line
Posterior Wall Myocardial Infarction is characterized by tall r waves in v1-v2 (mirror image) on ECG. Often missed, RCA or circumflex occlusion, isolated posterior MI is rare, use posterior leads V7-V9 for confirmation Primary management: STEMI protocol if confirmed with posterior leads showing ST elevation, emergent cardiac catheterization Key takeaway: This is a life-threatening emergency requiring immediate recognition and treatment - time-critical intervention saves lives
About the Author
Dr. Raj K
Emergency Medicine Physician Dr. Raj K is a board-certified Emergency Medicine physician with extensive experience in acute cardiac emergencies, advanced ECG interpretation, and critical care. He is passionate about medical education and bringing evidence-based emergency medicine knowledge to healthcare providers worldwide through E-PulsePoints. His clinical expertise includes STEMI management, complex arrhythmia recognition, and emergency cardiac procedures.